Stainless steel grade numbers identify the quality, durability, and the temperature resistance. The numbers associated with stainless steel grades and types also refer to the amount of Chromium, Nickel, Iron, Manganese, Titanium, etc, that make up the grade. For example, the number 316 contains 16%-18% Chromium and 11%-14% Nickel. The number 18/10 identifies the composition ratio of the stainless steel. These numbers refer to the amount of Chromium and Nickel percentages 18% and 10%. Stainless steel is used when corrosion and or oxidation is possible. A minimum of 12% Chromium lowers oxidation and corrosion resistance to the steel. Steel and the ferrous alloys within it will have a minimum of 12% Chromium for the resistance of corrosion, therefore is considered “Stainless Steel”. NOTE: Stainless Steel 304 is the most common. The main component of stainless steel is Iron, Chromium, and Nickel.
 Stainless Steel Grades and Types
Stainless Steel Grades and Types
Stainless Steel Grades Explained
Stainless Steel Types
Stainless Steel 300 Series: Austenitic Chromium Nickel Alloys
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 301:
Highly ductile for formed products and hardens rapidly during mechanical process.
-Has better wear resistance and fatigue strength than type 304.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 303:
Free machining version of type 304.
-Has the addition of sulfur and phosphorus.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 304:
The most common of austenitic grades which contain 8% nickel and 18% chromium.
-Used for chemical processing equipment, food industries, and beverage industries.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 316:
Contains 11% to 14% nickel and 16% to 18% chromium.
-Also has molybdenum added to the nickel and chrome of the 304 and the molybdenum is used to control “pit type attack”.
-Used in chemical processing, the pulp and paper industry, for food and beverage processing.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 317:
Contains higher percentage of molybdenum than 316 for high corrosive environments.
-Must have a minimum of 3% molybdenum.
-It is mostly used in stacks that contain scrubbers.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 321 and 347:
Developed for corrosive resistance to repeated exposure to temps above 800 degrees fahrenheit.
-321 is made by the addition of titanium.
-347 is made by the addition of tantalum and columbium.
-321 and 347 types are used primarily in the aviation industry.
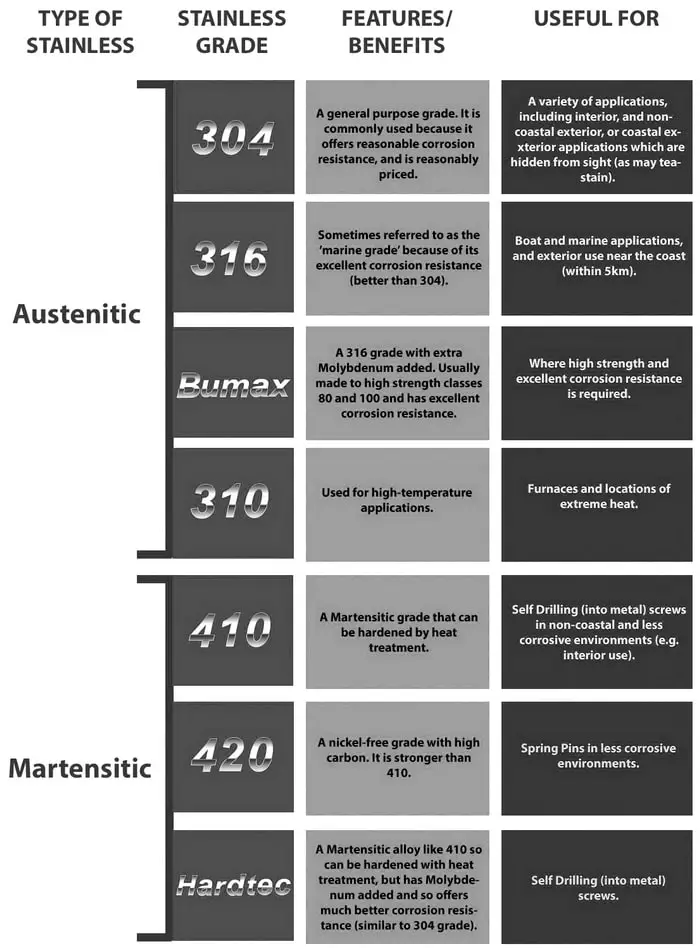 Types Of Stainless Steel CHART
Types Of Stainless Steel CHART
Stainless Steel 400 Series: Ferritic and Martensitic Chromium Alloys
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 405:
Lower chromium amount and added aluminum.
-Prevents hardening when cooled from high temps.
-Application includes heat exchangers.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 409:
Lowest chromium content of all stainless steels.
-Originally designed for muffler stock.
-Used for exterior parts in non critical corrosive environments.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 410:
Has the basic martensitic grade and contains the lowest alloy content.
-General purpose and heat treatable stainless steel.
-Used when corrosion is not severe.
-Applications include stressed parts needing strength and corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 410S:
Contains a lower carbon amount than Type 410.
-Improved weldability but lower harden ability.
-A general purpose corrosion and heat resisting chromium steel.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 414:
Has 2% nickel added for improved corrosion resistance.
-Applications include various springs and kitchen cutlery.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 416:
Has added phosphorus and sulphur to improve machinability.
-Applications include screws and machine parts.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 420:
Has more carbon to improve mechanical properties.
-Applications include medical and surgical instruments.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 430:
A basic ferritic grade with less corrosion resistance than 304.
-430 has high resistance to corrosives.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 431:
Has increased chromium for better corrosion resistance.
-Applications used in high strength parts (valves & pumps).
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 434:
Has molybdenum added for improved corrosion resist.
-Applications include automotive industry trims and metal fasteners.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 436:
Type 436 has columbium added in for better corrosion and heat resist.
-Applications include deep drawn parts.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 440:
More chromium and carbon added to improve toughness and corrosion resist.
-Applications include miscellaneous instruments.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 442:
Has more chromium to improve scaling resistance.
-Applications included are “heat” parts for furnaces and heaters.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 446:
Has more chromium introduced to improve corrosion at high temps.
-Best for oxidation resistance in a sulfuric atmosphere.
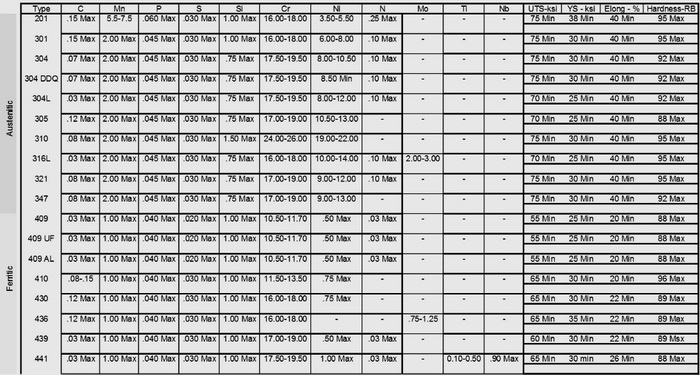 Stainless Steel Chemical and Mechanical Properties
Stainless Steel Chemical and Mechanical Properties
Stainless Steel 600 Series: Originally created for proprietary alloys. (No longer given SAE grade numbers)
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 601 through 604:
Martensitic low alloy steels.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 610 through 613:
Martensitic secondary hardening steels.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 614 through 619:
Martensitic chromium steels.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 630:
The most common PH stainless = known as 17-4
-17% chromium and 4% nickel.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 650 through 653:
Austenitic steels strengthened by hot and cold work.
Stainless Steel Grade/Type 660 through 665:
Austenitic superalloys = All grades but alloy 661 are strengthened by second phase precipitation.
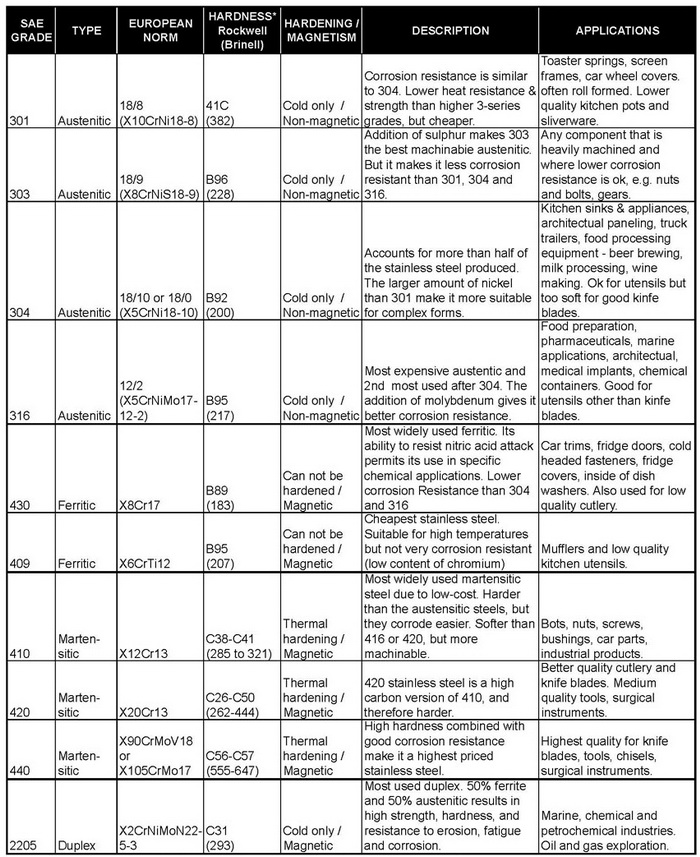 Stainless Steel Grades – Types Chart
Stainless Steel Grades – Types Chart
Carbon and Alloy Steel Types
Carbon steels and alloy steels are designated a four digit number.
-The first digit indicates the main alloying element.
-The second digit indicates the secondary alloying element.
-The last two digits indicate the amount of carbon, in hundredths of a percent by weight.
SAE designation and Type
1XXX = Carbon steels
2XXX = Nickel steels
3XXX = Nickel-chromium steels
4XXX = Molybdenum steels
5XXX = Chromium steels
6XXX = Chromium-vanadium steels
7XXX = Tungsten steels
8XXX = Nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels
9XXX = Silicon-manganese steels
Have more questions about stainless steel types and grades? Please leave a comment below and we will answer your questions.



Leave a Reply